本文由 AI 基于项目源码生成。
前言 在当今信息爆炸的时代,如何让用户更高效地获取和理解资讯内容成为了技术团队的重要挑战。传统的纯文本新闻阅读体验已经无法满足用户对信息直观性和交互性的需求。本文将深入解析我们团队开发的资讯可视化增强系统,分享如何将原始新闻文章转化为带有丰富可视化元素的交互式内容的完整技术实践。
这个系统的核心价值在于通过 AI 智能分析和前端可视化技术,自动识别文章中的关键信息,并为不同类型的内容匹配最合适的展示方式。无论是数值数据的可视化呈现,还是专业概念的即时解释,亦或是复杂事件的时间脉络梳理,系统都能自动完成,大大提升了用户的阅读体验和信息获取效率。
背景与需求 传统资讯阅读的痛点 在实际开发过程中,我们发现传统资讯阅读存在几个明显的痛点:
信息密度过高 :用户在面对大量文本内容时,很难快速抓住重点。特别是财经新闻中充斥着各种数值数据、专业术语和复杂概念,普通用户往往需要花费大量时间去理解。
交互体验缺失 :传统文章是线性的阅读体验,用户无法根据自己的需求深入探索感兴趣的内容。当遇到不懂的概念时,需要中断阅读去搜索引擎查找,严重影响了阅读的连贯性。
内容呈现单一 :即使是包含丰富数据的新闻,也只能通过纯文本的方式呈现,无法发挥数据可视化的优势。比如公司财报中的营收趋势、市场份额对比等,用图表呈现会更加直观。
技术挑战 在项目启动时,我们面临了几个关键的技术挑战:
内容理解的准确性 :如何让 AI 准确理解文章内容,识别出需要增强的关键信息?这涉及到自然语言处理的深层次应用。
展示方式的智能选择 :不同类型的内容适合不同的展示方式。数值数据适合用图表,概念解释适合用弹窗,时间事件适合用时间轴。如何自动做出最优选择?
前后端的协同工作 :后端的 AI 分析能力和前端的渲染能力如何有效配合,确保整个流程既高效又稳定?
性能和用户体验的平衡 :在增加大量可视化组件的同时,如何保证页面的加载速度和用户体验?
基于这些挑战,我们设计了一个完整的解决方案,通过两阶段处理流程和智能 Agent 系统,实现了从原始文章到增强内容的自动化转换。
技术方案
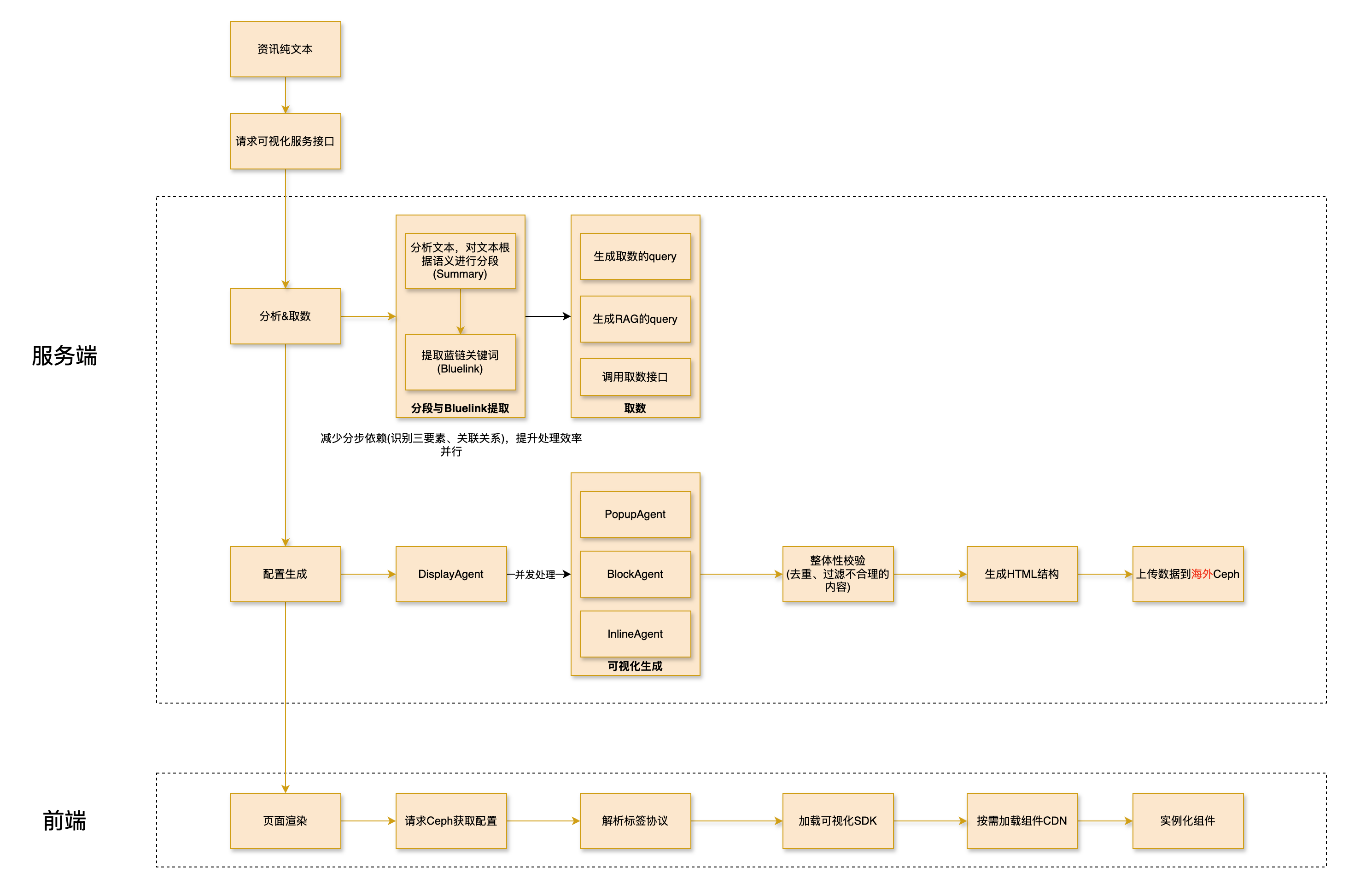
整体架构设计 我们采用了微服务架构,将整个系统分为后端 AI 处理服务和前端渲染服务两个主要部分:
后端服务 :基于 Spring Boot 构建,负责文章分析、AI 调用、数据获取等核心逻辑前端渲染 :基于 StencilJS 构建的 Web Components 系统,负责可视化组件的动态加载和渲染
两阶段处理流程 整个系统的核心是两阶段处理流程:
阶段一:分析与分类 (/news/classify接口)
接收原始文章并进行智能分段
调用大模型分析每个段落的内容特征
为每个段落分配合适的展示方式(inline、popup、block)
预获取相关数据,为下一阶段做准备
阶段二:增强与渲染 (/news/display接口)
根据分类结果调用对应的 Agent 生成具体内容
将生成的内容组装成可视化组件
返回最终的可视化配置
这种设计的优势在于将分析和生成分离,既提高了系统的可维护性,又为后续的调试和优化提供了便利。
智能 Agent 系统 我们设计了三种专门的 Agent 来处理不同类型的内容:
Inline Agent :处理数值数据的内联增强,如百分比、趋势数值等Popup Agent :处理专业概念的悬停解释,如金融术语、公司名称等Block Agent :处理复杂的图文卡片,如财务分析、时间脉络等
每个 Agent 都有专门的 Prompt 模板和工具调用能力,确保生成的内容质量符合预期。
深入实现 1. 文章智能分段算法 文章分段是整个流程的基础,我们需要将原始 HTML 文章切分成适合 AI 处理的文本块。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 private static final Pattern PUNCTUATION_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("[,;;。]|([,.]\\s)" );private static final Pattern LABEL_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("<[^>]*>" );private static List<String> splitTextWithPunctuation (String text) {new ArrayList <>();Matcher matcher = PUNCTUATION_PATTERN.matcher(text);int lastIndex = 0 ;while (matcher.find()) {int currentIndex = matcher.end();if (lastIndex < text.length()) {return result;
这个算法的关键点在于:
保留 HTML 结构 :通过正则表达式识别 HTML 标签,确保文章结构不被破坏智能标点分割 :根据中文和英文标点符号进行智能分割,保持语义完整性Chunk ID 管理 :为每个文本块分配唯一 ID,方便后续追踪和处理
2. 大模型分类策略 分类阶段的核心是通过精心设计的 Prompt 让大模型理解任务并做出准确的判断:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ClassifyDisplayInput classifyDisplayInput = new ClassifyDisplayInput (words, paragraphs, chunkListWithoutLabel);String classifyResultString = chatModelService.getDefaultChatClient()
我们在 Prompt 设计中重点考虑了:
明确的触发条件 :为每种展示方式定义了清晰的触发条件,减少模型的误判连续性约束 :确保每个 Agent 处理的文本块是连续的,避免内容碎片化数量控制 :限制各种 Agent 的处理数量,保证页面的简洁性
3. 数据预增强机制 在生成可视化内容之前,系统会预先获取相关的数据,这大大提升了生成内容的质量:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private DisplayAgentInput convert (ClassifyResult classifyResult, String content, List<String> splitList) {DisplayAgentInput displayAgentInput = new DisplayAgentInput ();if (classifyResult.getDisplayType() == BLOCK && !classifyResult.getDataQuery().isBlank()) {if (!data.isEmpty()) {return displayAgentInput;
这个机制的亮点在于:
按需获取 :只有需要数据的展示方式才会触发数据获取,避免不必要的网络请求异步处理 :数据获取和 AI 生成可以并行进行,提高处理效率错误容错 :即使数据获取失败,系统仍然可以继续处理,保证整体的稳定性
4. 前端组件工厂模式 前端渲染系统采用了工厂模式,根据配置动态创建不同类型的可视化组件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 export async function createComponent ( componentData: ComponentData Promise <HTMLElement > {const factory = factories.get (componentData.type );if (!factory) {throw new Error (`Unknown component type: ${componentData.type } ` );const element = await factory.create (componentData);setAttribute ('data-component-id' , componentData.id );setAttribute ('data-component-type' , componentData.type );setAttribute ('data-component-slot' , componentData.slot );return element;
这种设计的优势在于:
类型安全 :每个组件类型都有对应的工厂类,确保创建过程的类型安全可扩展性 :新增组件类型只需要添加对应的工厂类,不影响现有代码属性管理 :统一管理组件的通用属性,保证一致性
5. 动态组件加载器 为了实现按需加载和性能优化,我们设计了一个 sophisticated 的组件加载器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 export class ComponentLoader {private async loadComponent (componentType : string ,0 Promise <void > {try {const reg = this .currentConfig .umdRegistry ?.components ?.[componentType];if (reg) {await this .ensureRuntimeLoaded ();const deps = DEPENDENCY_MAP [componentType] || [];for (const dep of deps) {try {await this .loadDependency (dep);catch {}if (reg.umd ) {await this .loadScript (reg.umd );return ;const componentLoader = COMPONENT_MAP [componentType];if (!componentLoader) {throw new Error (`组件 ${componentType} 不存在` );await componentLoader ();catch (error : any ) {if (retryCount < this .currentConfig .retryOptions .maxRetries ) {const delay = this .currentConfig .retryOptions .exponentialBackoff this .currentConfig .retryOptions .retryDelay * Math .pow (2 , retryCount)this .currentConfig .retryOptions .retryDelay ;await new Promise ((resolve ) => setTimeout (resolve, delay));return this .loadComponent (componentType, retryCount + 1 );if (this .currentConfig .fallbackOptions .enableFallbacks ) {const fallbackComponent = FALLBACK_MAP [componentType];if (fallbackComponent) {await this .loadComponent (fallbackComponent);
这个加载器的核心特性包括:
多重加载策略 :支持 UMD、SystemJS、ESM 等多种加载方式智能重试机制 :采用指数退避算法进行重试,提高成功率降级处理 :当主要组件加载失败时,自动加载降级组件依赖管理 :自动加载组件所需的依赖,确保正确执行
核心接口与集成流程 系统接口概览 我们设计了三个核心接口来支持整个资讯可视化流程:
1. 分析与分类接口 (/news/classify)
功能 :接收原始文章,进行智能分段和展示方式分类输入 :NewsEnhanceRequest(包含 content、news_id、title)输出 :List<DisplayAgentInput>(分类结果和预获取数据)
2. 增强与渲染接口 (/news/display)
功能 :根据分类结果生成具体的可视化组件输入 :DisplayAgentInput(单个展示单元的完整信息)输出 :List<Map<String, Object>>(可视化组件配置)
3. 集成处理接口 (/news/vis)
功能 :一站式完成从原始文章到最终增强 HTML 的全流程输入 :NewsEnhanceRequest(完整请求参数)输出 :包含<datav>标签的最终 HTML 字符串
完整处理流程时序图 下面的时序图展示了从用户请求到最终返回增强文章的完整处理流程:
sequenceDiagram
participant User as 用户
participant Controller as NewsEnhanceController
participant Service as NewsEnhanceService
participant LLM as 大模型服务
participant Tools as 外部工具(RPC/RAG)
participant Ceph as Ceph存储
User->>+Controller: POST /news/vis<br/>(NewsEnhanceRequest)
Controller->>+Service: vis(request)
%% 阶段一:分析与分类
Service->>Service: 1. splitText(content)<br/>智能文本分段
Note right of Service: 基于标点符号和HTML标签<br/>将文章切分为Chunks
Service->>Service: 过滤HTML标签,<br/>生成Chunk列表
Service->>Service: 统计词数和段落数
Service->>+LLM: 2. 调用news_display_agent
Note left of LLM: 输入:文章特征+Chunks<br/>输出:展示类型分类结果
LLM-->>-Service: 返回ClassifyResult列表
%% 数据预增强
Service->>Service: 3. convert()转换处理
loop 遍历每个ClassifyResult
alt DisplayType == BLOCK 且有dataQuery
Service->>+Tools: queryToData(dataQuery)
Tools-->>-Service: 返回结构化数据
end
alt 有searchQuery
Service->>+Tools: rag(searchQuery)
Tools-->>-Service: 返回相关文章
end
end
Note right of Service: 生成DisplayAgentInput列表
%% 阶段二:并发增强处理
Service->>Service: 4. 并发处理所有DisplayAgentInput
par 并行处理
loop 每个DisplayAgentInput
alt DisplayType == POPUP
Service->>+LLM: PopupAgent生成
LLM-->>-Service: 弹窗组件JSON
else DisplayType == BLOCK
Service->>+LLM: BlockAgent生成
LLM-->>-Service: 图文卡片组件JSON
else DisplayType == INLINE
Service->>+LLM: InlineAgent生成
LLM-->>-Service: 内联增强组件JSON
end
end
end
%% 阶段三:结果重构
Service->>Service: 5. reconstructRawText()<br/>重构最终HTML
Note right of Service: 根据chunk_id排序<br/>将组件嵌入到原文中<br/>生成<datav>标签
loop 每个ClassifyResult
alt 需要上传到Ceph
Service->>+Ceph: uploadFile(componentData)
Ceph-->>-Service: 返回Ceph URL
Note right of Service: 生成外部存储格式的datav标签
else
Note right of Service: 生成内联数据格式的datav标签
end
end
Service-->>-Controller: 返回ProcessRecord<br/>(包含最终增强HTML)
Controller-->>-User: 返回增强后的文章<br/>(包含可视化组件)
阶段一:分析与分类的详细实现 1.1 文本智能分段处理 分段算法的核心挑战在于既要保持 HTML 结构的完整性,又要确保文本块的大小适合 AI 处理。实际代码位于NewsEnhanceService.java中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 private static final Pattern PUNCTUATION_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("[,;;。]|([,.]\\s)" );private static final Pattern LABEL_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("<[^>]*>" );private static List<String> splitTextWithPunctuation (String text) {new ArrayList <>();Matcher matcher = PUNCTUATION_PATTERN.matcher(text);int lastIndex = 0 ;while (matcher.find()) {int currentIndex = matcher.end();if (lastIndex < text.length()) {return result;
技术要点 :
HTML 标签保留 :通过LABEL_PATTERN识别并保留 HTML 结构语义完整性 :按中文标点(,;。)和英文标点(,.)分割Chunk 管理 :为每个文本块分配唯一 ID,支持后续追踪
1.2 大模型分类策略 分类阶段的 Prompt 工程是系统准确性的关键:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ClassifyDisplayInput classifyDisplayInput = new ClassifyDisplayInput (words, paragraphs, chunkListWithoutLabel);String classifyResultString = chatModelService.getDefaultChatClient()
分类结果结构 (基于实际项目的ClassifyResult类):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class ClassifyResult {private DisplayType displayType; private List<Integer> chunkIds; private String dataQuery; private String searchQuery; private String popupWord; private Object components;
1.3 数据预增强机制 在生成可视化内容前,系统会智能预获取相关数据:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 private DisplayAgentInput convert (ClassifyResult classifyResult, String content, List<String> splitList) {DisplayAgentInput displayAgentInput = new DisplayAgentInput ();if (classifyResult.getDisplayType() == BLOCK && !classifyResult.getDataQuery().isBlank()) {if (!data.isEmpty()) {if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(classifyResult.getSearchQuery())) {"\n" , articles));return displayAgentInput;
阶段二:增强与渲染的 Agent 系统 2.1 专门的 Agent 设计 我们为三种不同的展示方式设计了专门的 Agent:
Block Agent - 复杂图文卡片生成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Component public class BlockAgentService {public Object generate (DisplayAgentInput input) {String prompt = promptService.getPrompt(PromptFileName.NEWS_BLOCK_AGENT);BlockAgentRequest request = new BlockAgentRequest ("" , input.getChunkContents()),String result = chatModelService.getDefaultChatClient()return JsonUtil.parse(result, new TypeReference <List<Map<String, Object>>>() {});
Popup Agent - 悬停解释卡片生成
专注于专业概念的即时解释
集成图片获取和相关链接生成
支持智能触发规则匹配
Inline Agent - 数值数据内联增强
处理百分比、趋势数值等
生成简洁的数值可视化
保持阅读流的连贯性
2.2 并发处理优化 为了提高处理效率,我们使用ForkJoinPool进行并发处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool (Math.min(displayAgentInputList.size(), 8 ));try {Object component = display(displayAgentInput, request.getModelProvider());int i = displayAgentInputList.indexOf(displayAgentInput);catch (Exception e) {"组件生成失败: {}" , displayAgentInput.getDisplayType(), e);if (request.isDebug()) {throw e;new CompletableFuture [0 ])).join();
最终 HTML 重构与组件注入 3.1 智能文本重构 重构算法确保生成的可视化组件正确嵌入到原文中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 private String reconstructRawText (List<String> splitList, List<ClassifyResult> classifyResults) {0 )))StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder ();int currentIndex = 0 ;for (ClassifyResult resultItem : sortedResults) {while (currentIndex < resultItem.getChunkIds().get(0 )) {String componentHtml = generateComponentHtml(resultItem);if (resultItem.getDisplayType() == BLOCK) {else {1 ) + 1 ;while (currentIndex < splitList.size()) {return result.toString();
3.2 <datav>标签格式设计 最终生成的<datav>标签支持两种格式:
内联数据格式 :
1 2 3 <datav data ='{"display":"BLOCK","components":[{"type":"chart","chart_type":"bar","data": [...]}]}' > </datav >
外部存储格式 (避免数据过大):
1 2 3 <datav data ="https://cdn.ainvest.com/icon/ownership/xxxxxxxx.txt" > </datav >
关键技术深度解析 1. Prompt 动态管理机制 我们的 Prompt 系统支持远程动态更新,确保 AI 能力的持续优化:
远程获取机制 :
Prompt 存储在 Gitee 仓库中,支持版本控制
通过 HTTP 请求动态获取最新 Prompt
内存缓存+定时刷新(每分钟自动更新)
缓存策略 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 @Service public class PromptService {private final Map<PromptFileName, String> promptMap = new ConcurrentHashMap <>();@Scheduled(cron = "0 0/1 * * * ?") public void refresh () {for (PromptFileName promptFileName : PromptFileName.values()) {public String getPrompt (PromptFileName promptFileName) {if (promptMap.containsKey(promptFileName)) {return promptMap.get(promptFileName);else {String prompt = getLatestPrompt(promptFileName);return prompt;public String getLatestPrompt (PromptFileName promptFileName) {String url = "https://gitee.com/visionzhao/new_vis_prompts/raw/main/" + promptFileName.getFileName();new HashMap <>();"User-Agent" , "Mozilla/5.0" );try {return rpcService.get(url, headers);catch (Exception e) {throw new NewVisException (ErrorCode.PROMPT_ERROR, promptFileName.getFileName());
2. 外部数据集成系统 2.1 结构化数据查询 DataVisTools.queryToData方法负责获取数值化数据:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public List<Map<String, Object>> queryToData (String query) {try {return rpcService.post(Url.QUERY_TO_DATA,new BaseLlmRequest (query),new TypeReference <>() {});catch (Exception e) {"数据获取失败,返回空列表: {}" , query);return List.of();
数据格式示例 (基于实际接口返回格式):
1 2 3 4 [ { "日期" : "2023-01-01" , "股票代码" : "00700.HK" , "收盘价" : 350.0 } , { "日期" : "2023-01-02" , "股票代码" : "00700.HK" , "收盘价" : 352.5 } ]
接口实现 (基于DataVisTools.java的实际代码):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public List<Map<String, Object>> queryToData (String query) {return rpcService.post(Url.QUERY_TO_DATA,new BaseLlmRequest (query),new TypeReference <>() {});
2.2 RAG 检索系统 RagTools.rag方法负责获取相关文档:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public List<String> rag (String query, String... channels) {try {RagRequest request = new RagRequest ();0 ? channels :new String []{"WEB_EN" , "REPORT" , "NEWS" });return rpcService.post(Url.RAG_QUERY, request,new TypeReference <>() {});catch (Exception e) {"RAG检索失败: {}" , query, e);return List.of();
3. 前端组件工厂模式 前端渲染系统确实采用了工厂模式设计,位于HIVIS/src/core/ComponentFactory.ts中。实际代码使用 Map 注册表管理各种组件工厂:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 const factories = new Map ();set ('text' , new TextComponentFactory ());set ('chart' , new ChartComponentFactory ());set ('link' , new LinkRowComponentFactory ());set ('link-row' , new LinkRowComponentFactory ());set ('ntv' , new NtvComponentFactory ());set ('image' , new ImageComponentFactory ());set ('timeline' , new TimelineComponentFactory ());export async function createComponent ( componentData: ComponentData Promise <HTMLElement > {const factory = factories.get (componentData.type );if (!factory) {throw new Error (`Unknown component type: ${componentData.type } ` );const element = await factory.create (componentData);setAttribute ('data-component-id' , componentData.id );setAttribute ('data-component-type' , componentData.type );setAttribute ('data-component-slot' , componentData.slot );return element;
每个具体组件工厂都有独立的类,如TextComponentFactory负责创建data-vis-text组件,ChartComponentFactory负责创建aigc-chart组件等。
4. 动态组件加载器 项目中确实存在动态组件加载器,位于HIVIS/src/core/component-loader.ts。这是一个功能完整的加载器,支持多种加载策略:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 export class ComponentLoader {private async loadComponent (componentType : string ,0 Promise <void > {try {const timeout = new Promise <never >((_, reject ) => {setTimeout (() => {reject (new Error (`加载组件 ${componentType} 超时` ));30000 ); const loadPromise = (async () => {const reg = this .currentConfig .umdRegistry ?.components ?.[componentType];if (reg) {await this .ensureRuntimeLoaded ();const deps = DEPENDENCY_MAP [componentType] || [];for (const dep of deps) {try {await this .loadDependency (dep);catch {}if (reg.umd ) {await this .loadScript (reg.umd );return ;const componentLoader = COMPONENT_MAP [componentType];if (!componentLoader) {throw new Error (`组件 ${componentType} 不存在` );await componentLoader ();await Promise .race ([loadPromise, timeout]);catch (error : any ) {const { maxRetries, retryDelay, exponentialBackoff } =this .currentConfig .retryOptions ;if (retryCount < maxRetries) {const delay = exponentialBackoffMath .pow (2 , retryCount)await new Promise ((resolve ) => setTimeout (resolve, delay));return this .loadComponent (componentType, retryCount + 1 );if (this .currentConfig .fallbackOptions .enableFallbacks ) {const fallbackComponent = FALLBACK_MAP [componentType];if (fallbackComponent) {await this .loadComponent (fallbackComponent);
该加载器支持 UMD/SystemJS/ESM 多种加载方式,具备重试机制、降级处理和依赖管理功能。
踩坑经验 1. AI 输出的不稳定性 在实际开发中,我们发现大模型的输出格式并不总是稳定的,这给后续的 JSON 解析带来了挑战。
问题表现 :
有时会在 JSON 前后添加解释性文字
有时会使用中文而不是英文
有时会包含注释或不必要的空格
解决方案 :
1 2 3 4 5 new TypeReference <>() {}
同时,我们在 Prompt 中强调了输出格式的要求:
必须是压缩的 JSON 格式
不包含任何解释或注释
统一使用英文
2. 前端组件的生命周期管理 在开发过程中,我们遇到了前端组件生命周期管理的复杂问题。
问题表现 :
组件在动态加载时可能出现时序问题
多个相同类型的组件可能出现状态混乱
组件销毁时可能出现内存泄漏
解决方案 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 export class DataV {private resizeObserver : ResizeObserver | null = null ;private setupResizeObserver (): void {if ('ResizeObserver' in window ) {this .resizeObserver = new ResizeObserver (() => {emit ('viz-resize' , {componentId : 'datav-root' ,timestamp : Date .now (),data : {width : this .el .clientWidth ,height : this .el .clientHeight ,this .resizeObserver .observe (this .el );private cleanup (): void {if (this .resizeObserver ) {this .resizeObserver .disconnect ();this .resizeObserver = null ;this .destroyPopupContainer ();disconnectedCallback (this .cleanup ();
3. 并发处理的性能优化 在处理长文章时,并发处理多个文本块会带来性能挑战。
问题表现 :
同时发送大量请求给 AI 服务可能导致限流
前端同时渲染多个组件可能导致页面卡顿
内存占用过高可能影响用户体验
解决方案 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 try {Object component = display(displayAgentInput, request.getModelProvider());int i = displayAgentInputList.indexOf(displayAgentInput);catch (Exception e) {if (request.isDebug()) {throw e;
4. Prompt 工程的迭代优化 Prompt 工程是一个需要不断迭代优化的过程。
问题表现 :
初始版本的 Prompt 过于复杂,AI 难以理解
输出结果不够稳定,格式时有变化
某些边界情况处理不当
解决方案 :
简化指令 :将复杂的指令拆分成多个简单的部分示例驱动 :提供清晰的输入输出示例约束明确 :明确指定输出的格式和限制持续监控 :建立监控机制,及时发现问题
5. 数据获取的容错处理 在获取外部数据时,网络不稳定和数据格式变化是常见问题。
问题表现 :
外部 API 响应缓慢或不稳定
数据格式发生变化导致解析失败
网络超时影响用户体验
解决方案 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public List<Map<String, Object>> queryToData (String query) {try {return rpcService.post(Url.QUERY_TO_DATA,new BaseLlmRequest (query),new TypeReference <>() {});catch (Exception e) {"数据获取失败,返回空列表: {}" , query);return List.of();
参考资料 技术栈和工具
Spring Boot : 后端框架StencilJS : 前端 Web Components 框架TypeScript : 前端开发语言Jackson : JSON 处理库Web Components : 前端组件标准
相关文档和链接
通过这个项目,我们深刻体会到 AI 技术与前端可视化结合的巨大潜力。虽然过程中遇到了不少挑战,但每解决一个问题,系统就变得更加健壮和完善。希望我们的经验能够对正在探索类似领域的开发者有所启发和帮助。
在实际开发中,我们发现最重要的是保持系统的模块化和可扩展性。AI 技术在快速发展,我们的架构需要能够快速适应新的模型和能力。