技术拆解-股权洞察与企业架构
业务说明
股权洞察
分为了左右两部分:左边是股权分布,右边是企业投资情况分布。
技术储备
D3.js
descendants
merge
tree
nodeSize
separation
SVG
滤镜(feComponentTransfer、filter)
左右树(我自己造的名词)
接口
请求单个节点
接口维护人员:范智强
以股权洞察为例:
1 | |
请求多个节点
数据结构
程序数据结构
d3.hierarchy
Node
是 D3 的HierarchyNode<Datum>对象
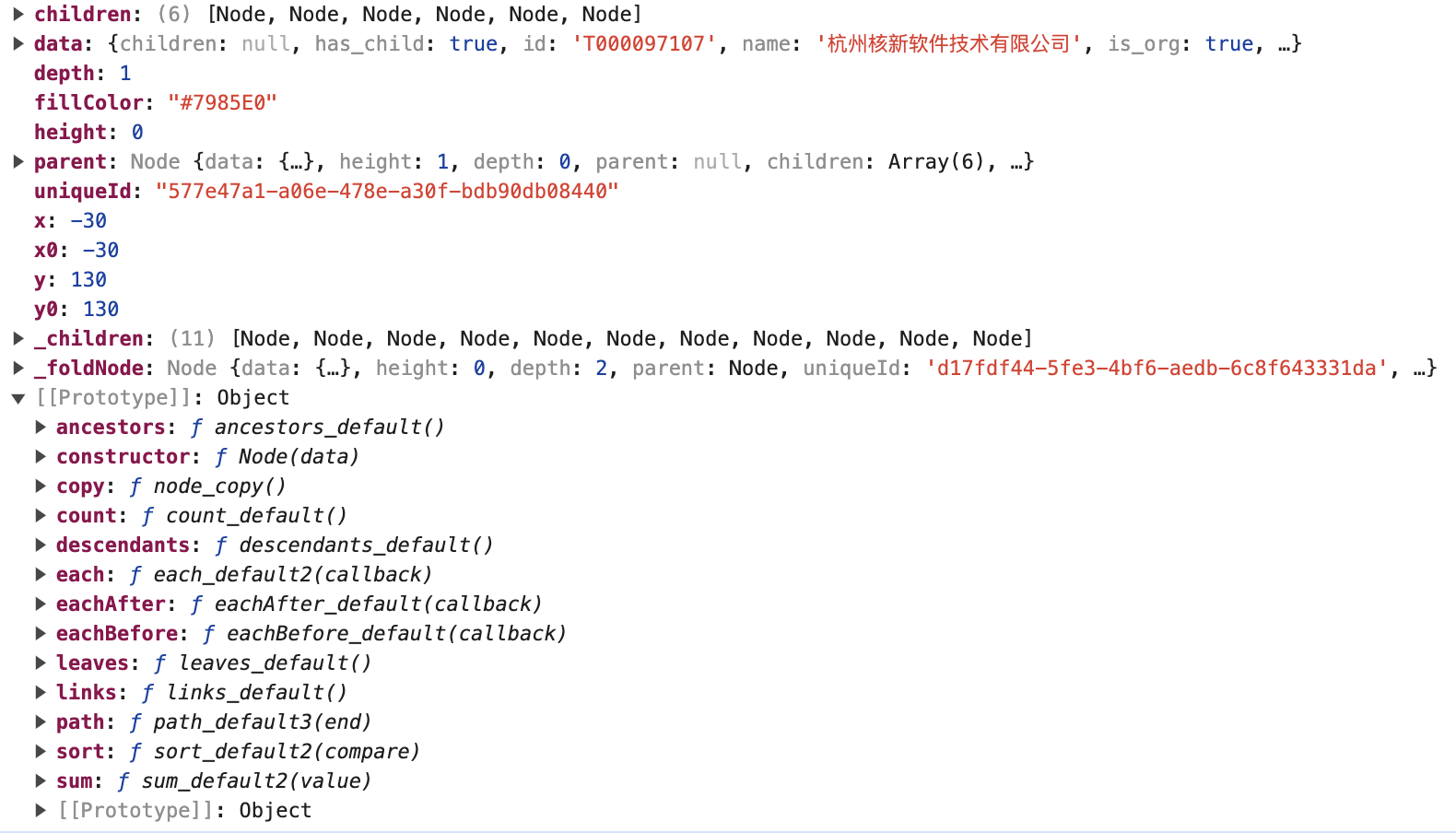
HierarchyNode
1 | |
1 | |
额外扩展的字段
maxLeft:左侧最大节点数maxRight:右侧最大节点数specialType:特殊节点,比如’fold’_foldNode:折叠的节点_children:子节点数据,可以用来判断在点击时要不要请求后端数据photo:logo 图片x0:记录上一次的位置y0:记录上一次的位置
更多
程序流程
- 请求接口获取数据
- 将数据拆分为左右两部分
- 将数据处理为带有
更多的格式 - 通过 d3.hierarchy 将数据处理为层级结构
- 添加缩放事件
- 设置画布的样式
关键函数和方法
请求数据
fetchData()
展开子节点
update() -> on(‘click’)->this.clicked(d)->this.fetchData(d).then((d) => doNext());fetchData(d)
展开更多节点
通过foldLimit配置项来控制展开的数量,每次都会额外展开foldLimit个节点。
fetchData()中的特殊处理:
1 | |
1 | |
显示全部
expand():全流程,包含取数、数据加工、渲染
fullExpand():纯数据加工,不包含取数
fetchEquityData():取数,获取股权数据,这里做了合并请求(过滤尚未请求数据的节点,拼接 url 参数,一次性请求)
update():渲染
放大缩小
1 | |
聚焦
截图
只看上市
恢复默认
切换黑白风格
如何实现自定义事件?
1 | |
布局
用的d3.tree()
1 | |
通过nodeSize确定节点大小,包括间隙。这就是为什么上面设置的高度 130 大于宽度 60,而实际上我们最终看到的画出来的节点宽度却是大于高度的。
这是因为默认计算的是纵向树,而我们把它旋转了 90 度,变成了横向树,因此高宽的设置是对调的。
1 | |
绘制
绘制带 logo 的节点(机构方形 rect,人员圆形 circle)
d3.tree()计算布局
对左右两边的线进行动画、布局的设置
绘制线条
绘制文字(文字依赖于线条的定位)
节点热区处理
绘制展开/收起子节点的图标
绘制节点:
createNodeShape()普通节点
展开收起节点
节点
几何图形
图片 logo
data.photo
文字
超过 8 个文字换行处理;超过 16 个文字…显示
标签 labels
连线
在update()中。
通过起点+2 个拐点+终点来绘制线段。
1 | |
连线的动画是默认的 D3 过渡动画。
linkUpdate
.attr(‘d’的重复代码太多了!!!
线上的文字(难点)
link 的text属性。
绘制一条看不见的线用来获取线的长度及对应点的坐标,从而计算文字的位置。
代码量不少。
箭头等 icon 也是这里绘制的。
transform 定位,左右的节点不一样。
textUpdate
动画
一些技巧
怎么样才能提升阅读代码的速度?
初期将交互和样式设计先绑定好
这样后面执行交互需要筛选数据的时候,就可以快速通过样式去选择元素了。
bind
call
depth 属性的设计
分组
先把所有元素规划好分组
变量命名
可以通过加下划线前缀来标注私有属性
给所有样式添加一个固定前缀
避免和页面其他样式重名。
记录上一次的位置
1 | |
移动端组件通用需求
缩放上下限
可以改进的地方
将数据处理完全独立出来
现在还是很多耦合在代码里的
可以抽取为公共库和函数的内容
- 组件的事件绑定
待确认的需求
需不需要全部显示的功能?
后端需要提供批量请求节点的接口
经验教训
一定要套个容器(DIV)
这次出现了 2 个问题:
1、接入 KAmis,发现因为给 SVG 设置了 position:fixed,导致绘图层和点击后的蒙层飘到页面看不见的地方去了;
2、接入 AIGC 的示例页面,发现因为我是在初始化传入的 DOM 下面直接画 SVG 的,而 AIGC 页面传入的 DOM 没设置 positon,导致点击后,蒙层定位就出问题了。
所以写组件,一定要有容器的概念,主动套个 DIV,且将其和子元素的定位设置为子绝父绝 与页面其他元素进行隔离,然后在 DIV 里面画 SVG。
1 | |
非必要不依赖
比如请求数据,用了 axios 这个库,后面又要花时间去掉这个依赖,改为 fetch